Topic: Relationships Among Organisms
Relationships Among Organisms
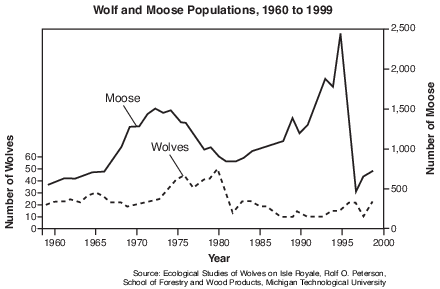
An observable trend in the wolf and moose data between 1980 and 1995 is
(1) as the wolf population decreases, the moose population increases
(2) as the wolf population decreases, the moose population decreases
(3) the numbers of wolves and moose are relatively constant
(4) the numbers of wolves and moose appear to be unrelated
Maple leaf beetles and willow leaf beetles are named for the type of tree where they live and reproduce. They look identical to each other when observed, but experiments have shown that willow beetles would starve before eating maple leaves. This is an example of specialization that would directly reduce
(1) variation
(2) competition
(3) adaptation
(4) replication
Which statement represents a characteristic of an ecosystem that is not likely to sustain itself?
(1) The Sun provides the needed energy.
(2) Energy is transferred from plants to animals.
(3) There are more consumers than producers.
(4) There are interactions between biotic and abiotic factors.
Puppies are often given medicine to eliminate roundworms from their intestines. These worms consume some of the food the puppies have digested. The worms and the puppies represent a relationship known as
(1) predator–prey
(2) consumer–producer
(3) parasite–host
(4) autotroph–heterotroph

Which statement best describes a function of the molds, bacteria, and yeasts in this ecosystem?
(1) They convert light energy into chemical energy.
(2) They carry out a food-making process, using inorganic raw materials.
(3) They break down dead organisms, releasing raw materials to the environment.
(4) They act as catalysts to speed up the energy flow between organisms.
Grasses → Elk → Wolves
Wolves in the park were killed or driven off by humans in the 1920s and 1930s. In the winter of 1995, humans released 17 wolves from Canada into the park. A year later, 14 more wolves were released.
One possible reason that the wolves were released into the park was to
(1) eliminate unwanted autotrophs
(2) reduce an overpopulation of elk
(3) provide food for small predators
(4) increase the number of herbivores
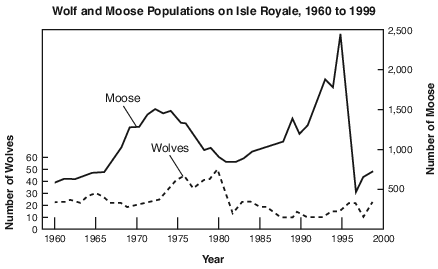
What is the relationship between a wolf and a moose?
(1) wolf–prey; moose–predator
(2) wolf–parasite; moose–host
(3) wolf–predator; moose–decomposer
(4) wolf–predator; moose–prey
Tissues of oleander plants contain chemicals that are poisonous to many mammals. The production of these poisonous chemicals most likely benefits oleanders by preventing leaf loss caused by
(1) lack of rain
(2) scavengers
(3) mineral absorption
(4) herbivores
Found: A Plant-Eating Spider
Spiders are meat-eaters. Until recently, scientists thought that was true for the roughly 40,000 spider species in the world. Now, researchers have discovered a spider that eats mostly plants.
Bagheera kiplingi, a jumping spider, lives in Central America and Mexico. It nests in the leaves of acacia shrubs. Scientists have long known that ants live in these plants. The ants eat the plants’ little yellow vegetables. But scientists had no idea that the spiders eat the vegetables too.
Christopher Meehan was a college student when he found the plant nibbling spiders. “I thought I was hallucinating,” he told TFK (Time for Kids). “But by the end of the day, I had seen about 100 more spiders eating plants.”
Source: Time for Kids World Report,
Edition 10/23/09 Vol. 15, #7 p.3
Which row best characterizes Bagheera kiplingi and acacia shrubs?
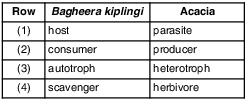
(1) 1
(2) 2
(3) 3
(4) 4
An ecosystem is self-sustaining as long as organ- isms have sufficient quantities of energy, oxygen, minerals, and water. When organisms die, some of these materials are recycled back to plants in the ecosystem primarily through the activity of
(1) predators
(2) decomposers
(3) pathogens
(4) parasites

Grasshopper Mice
In the Sonoran Desert in the southwestern United States, the grasshopper mouse is active at night, searching for crickets, rodents, tarantulas, and even scorpions. The mouse ignores the venom of the scorpion, kills it, and consumes its flesh. The ability of the mouse to ignore the pain normally associated with the venom of the scorpion is due to the presence of a mutated protein. This protein prevents the pain signal from reaching the brain.
These mice are born killers, capable of taking down prey that are much larger than themselves. They are also aggressive neighbors and take over nests by displacing other desert inhabitants rather than making their own. Under difficult environmental conditions, they may even eat members of their own species.
Identify one advantage to grasshopper mice of being active during the night rather than daylight. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Their hunting is not affected by the extreme heat during the day.
• — They are better able to sneak up on prey in the dark.
• — They are not as likely to be dehydrated by the hot Sun and will need less water.
• — Their prey are active at night.
• — They are less visible to predators/prey.
Species A, B, C, and D are all different heterotrophs involved in the same food chain in an ecosystem. The table below shows the population of each of these species on one summer day.
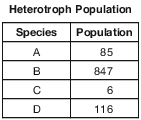
There are groups of organisms that must be present in this ecosystem that are not shown in the table. Identify one of these groups of organisms and state the role of this group in this ecosystem. [1]
Group: ________________________________________
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — producers; capture energy from the Sun
• — producers; provide food for other organisms in the ecosystem
• — decomposers; recycle the remains of dead organisms
• — bacteria; recycle nutrients/raw materials
• — fungi; decompose dead organisms
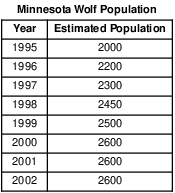
Directions: Using the information in the data table, construct a line graph on the grid, following the directions below.
Wolves prey on animals such as deer. Identify one adaptation of deer that would help them to survive in an area populated by wolves. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — speed
• — antlers
• — hooves for protection/defense
• — fur color similar to surroundings
• — well-developed senses
Types of Predators
When large predators, such as lions or wolves, are removed from a food web, smaller “mesopredators” step in to take their places, and the results may be severe. Mesopredators are usually smaller and more numerous than the larger “apex” predators that they replace. Some are also omnivores, eating plant and animal food sources, rather than eating the meat-only diet of the largest predators. Examples of mesopredators include coyotes, raccoons, and skunks.
In 1874, General George Custer noted that there was an abundance of wolves, but few coyotes, in South Dakota. Today, there is an abundance of coyotes, but no wolves. The wolves were removed to protect domestic sheep, but now the coyotes are often responsible for attacking sheep and other animals. The cost of controlling mesopredators by human intervention can be very high, as mesopredators are very numerous and quickly “bounce back” after control efforts. Meanwhile, the number of apex predators that are endangered continues to increase.
State how the mesopredator population was most likely controlled before the wolves were removed from the food web. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The wolves ate the mesopredators.
• — The “apex” or top predator was at the top of the food pyramid and fed on the levels below.
• — competition for food
Both food chains and food webs can be used to illustrate relationships between organisms in an ecosystem.
Discuss these methods of representing relationships. In your answer, be sure to:
• state one similarity in the way relationships between organisms are shown in food chains and food webs [1]
• explain why using a food chain is more limiting than using a food web to show relationships between organisms in an ecosystem [1]
The student’s response to the bulleted items in the question need not appear in the following order.
• 15 Allow 1 credit for stating one similarity in the way relationships between organisms are shown in food chains and food webs. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Both show which organisms feed on other organisms.
• — Both illustrate how energy flows from one organism to another through an ecosystem.
• 16 Allow 1 credit for explaining why using a food chain is more limiting than using a food web to show relationships between organisms in an ecosystem. Acceptable responses include, but are not lim- ited to:
• — Food chains only show one specific series of feeding relationships.
• — Food webs show the feeding relationships more completely.
• — Food webs show more ways that energy can flow through the ecosystem.
• — Food webs show that organisms eat more than one type of food.
